Intel Bolsters CPU Security with Memory Encryption Technologies
Intel has pledged to significantly enhance the security of its processors by implementing full memory encryption and other crucial security improvements, addressing vulnerabilities exposed by exploits like Meltdown and Spectre. These enhancements aim to mitigate exploits that leverage vulnerabilities in processor engineering processes such as out-of-order execution (OOOE), branch prediction, and speculative execution, which are designed to improve performance.
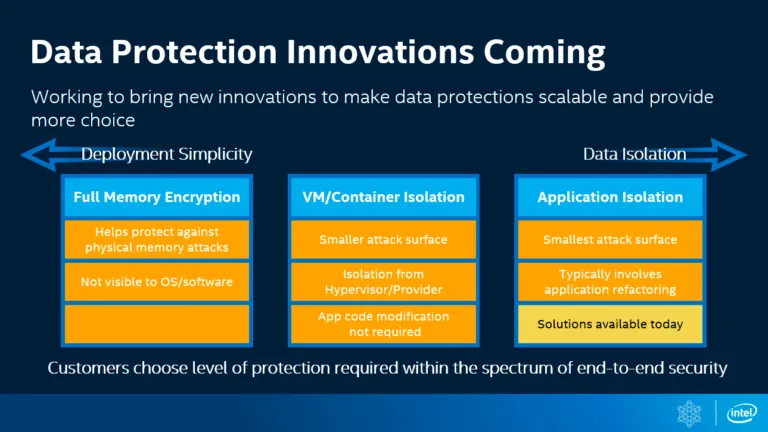
Intel’s Software Guard eXtensions (SGX) is one approach to protecting processors from these vulnerabilities. SGX is a hardware encryption technology that creates a “secure enclave” within a portion of the memory, providing a protected space for sensitive data. This technology will be available on both consumer and enterprise processors.
 Intel SGX explained
Intel SGX explained
However, SGX has limitations. As Ars Technica has previously analyzed, SGX only functions on Intel processors, requires developers to specifically design applications to utilize it, and has a limited memory capacity (up to 128MB) for designating data as “top secret.”
In contrast, AMD’s Secure Memory Encryption (SME) and Secure Encrypted Virtualization (SEV) offer greater flexibility. SME encrypts all system RAM without requiring application updates from developers, and it has less of a performance impact than SGX.
 Comparing Intel and AMD security technologies
Comparing Intel and AMD security technologies
Intel is addressing these limitations with Total Memory Encryption (TME) and Multi-Key Total Memory Encryption (MKTME). These technologies offer a more comprehensive approach to memory encryption, although they are not yet available in current-generation Intel processors. Despite these ongoing security concerns, Intel has previously maintained that its CPUs remain a strong choice compared to AMD.
Intel’s commitment to enhancing CPU security with full memory encryption and other improvements represents a significant step towards mitigating vulnerabilities and protecting user data. While technologies like SGX offer some level of protection, the forthcoming TME and MKTME promise more comprehensive security measures. These advancements aim to address the evolving landscape of security threats and provide users with greater confidence in the protection of their sensitive information.
References:



Comments (0)